Alo guys...how is everything?..hehe..okey, in this post I willm share with all of you about the thing that I learned in the third class..
1st of all, we learned about computer network..computer networking is connecting a computer
with other computers or other devices to enable them to communicate with each other.
There are 4 main network classification which are LAN(Local Area Network), MAN(Metropolitan Area Network), WAN(Wide Area Network) and PAN(Personal area Network).
Then, we learned about network components which are the terminals and workstation or end node, the software to control data transmission, transmission media, network electronics, and network architecture standards.
Terminals and workstation normally refers to data sources and destinations.
Transmission media is for transmitting data and control signals. There are two types of transmission media which are guided or bounded and unguided or unbounded(air/vacuum).
Network electronics devices are devices that controls data transmission from
sources to destination. They also act as interface between different transmission media or communication protocol. Some of them are hub, router, switch, bridge and gateway.
Hub
You wanna know more about hub??..visit this link..http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2/topics/networks/network%20components/network_components/hub.htm
this link for bridge, guys..:)..http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2/topics/networks/network%20components/network_components/bridges.htm
switch :http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2/topics/networks/network%20components/network_components/switches.htm router : http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2/topics/networks/network%20components/network_components/routers.htm
gateways : http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2/topics/networks/network%20components/network_components/gateways.htm
Then, we learned about topology networking..do you actually know the meaning of network topology?
Well, basically network topology is the study of the arrangement or mapping of the elements
(links, nodes, etc.) of a network, especiallythe physical (real) and logical (virtual) interconnections between nodes.
There are two types of network topology which are :-
1) Physical topology
2) Logical topology
Physical topology is the way that the workstations are connected to the network through the actual cables that transmit data the physical structure of the network. Logical topology is the mapping of the flow of data between the nodes in the network determines the logical topology of the network.
visit this link to get more information about topology..http://fcit.usf.edu/network/chap5/chap5.htm
Then we learned about network equipment. Network equipment is actually all computers, peripherals, interface cards and other equipment needed to perform data-processing and communications within the
network. They are :
File Server
Workstation
Network Interface Cards
Concentrator/Hubs
Repeater
Bridges
Routers
Switch
A file server stands at the heart of most networks and it is a very fast computer. See this to learn more about it and also other kind of server. http://www.teach-ict.com/as_a2/topics/networks/network%20components/network_components/servers.htm
Next, we have workstations. Do you know what a
workstation is? If a computer is connected to a network, we can call that
computer as a workstation. They don’t have storage capability but the files
that we want to save could be saved on the file server. Almost any computer can
serve as a network station. Click to the given URL to find out more about
workstation….
 and
and

Do you know what a protocol is?..
Well, a protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network.
These rules include guidelines that regulate the following characteristics of a network:
– access method,
– allowed physical topologies,
– types of cabling, and
– speed of data transfer
Protocol or communication protocol means it will standardize the specifically address how the devices on a network communicate.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and described how data is moved across the network.
• Ethernet, LocalTalk, Token ring for wired networks
• TCP/IP and WAP for internet
• Wi-Fi for wireless networks
• Bluetooth, for short range wireless network


2. Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable



3. Coaxial Cable
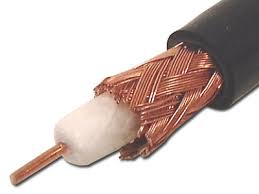
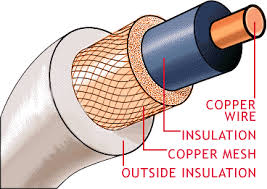
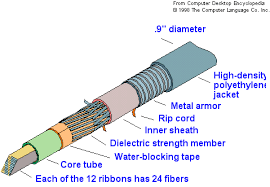
4. Fibre Optic Cable

Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
The cable has four pairs of wires inside the jacket. Each pair is twisted with a different number of twists per inch to help eliminate interference from adjacent pairs and other electrical devices. See more...
Here is the summary or the ethernet cabling:
Then, we learned about Network Operating System.
Network operating system is
• Software that controls a network and its message (e.g. packet) traffic and queues, controls access
by multiple users to network resources such as files, and provides for certain administrative functions, including security.
There are two major types of network operating system. They are peer-to-peer system and client/server system. Click here to know more about them.
I think that's all for now..till then,,goodbye..>.<
Next is network interface card or NIC. NIC is provides
the physical connection between the network and the computer workstation. NIC
also determines the speed and the performance of a network. There are three
most common NIC are
localtalk
connectors,
ethernet cards
token
ring cards.
You can read more about them here..:)
Protocol
Well, a protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network.
These rules include guidelines that regulate the following characteristics of a network:
– access method,
– allowed physical topologies,
– types of cabling, and
– speed of data transfer
Protocol or communication protocol means it will standardize the specifically address how the devices on a network communicate.
Logical topologies are bound to network protocols and described how data is moved across the network.
• Ethernet, LocalTalk, Token ring for wired networks
• TCP/IP and WAP for internet
• Wi-Fi for wireless networks
• Bluetooth, for short range wireless network
Ethernet
Early Ethernet network were half duplex, uses an access method
called CSMA/CD (Carrier Sense Multiple Detection) Access/Collision Detection),
a system where each computer listens to the cable before sending anything
through the network to avoid collisions.
Since 1997 Ethernet uses full duplex communication, that does
not require listening to other messages and no collisions occur.
Localtalk
• a network protocol that was developed Macintosh computers.
• used a method called CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multiple Access
with Collision Avoidance), where ), computer signals its intent to transmit
before it
actually does so.
• allows for linear bus, star, or tree topologies using twisted
pair cable.
• disadvantage : slow speed (only 230 Kbps).
Token Ring
• developed by IBM in the mid-1980s.
• access method involves token-passing.
• the computers are connected so that the signal travels around
the network from one computer to another in a logical ring.
• A single electronic token moves around the ring from one
computer to the next. If a computer does not have information to transmit, it
simply passes the token on to the next workstation. If a computer wishes to transmit
and receives an empty token, it attaches data to the token. The token then
proceeds around the ring until it comes to the computer for which the data is meant-
the data is captured by the receiving computer.
FDDI
• Fiber Distributed Data Interface - a network protocol that
is used primarily to interconnect two or more local area networks, often over large
distances.
• access method involves token-passing.
• uses a dual ring physical topology. Transmission normally
occurs on one of the rings; if a break occurs, the system keeps information
moving by automatically using portions of the second ring to create a new
complete ring.
• A major advantage of FDDI is speed. It operates over fiber
optic cable at 100 Mbps.
You could find more about protocol here:………………………
Now, let’s move on to cable!!!!!
CABLING
Cable or cable is the medium through which information
usually moves from one network device to another.
There
are four types of cables which are:
1. Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
Cable
3. Coaxial Cable
4. Fibre Optic Cable
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable
The cable has four pairs of wires inside the jacket. Each pair is twisted with a different number of twists per inch to help eliminate interference from adjacent pairs and other electrical devices. See more...
Here is the summary or the ethernet cabling:
| SPECIFICATION | CABLE TYPE | MAXIMUM LENGTH |
|---|---|---|
| 10BaseT | Unshielded Twisted Pair | 100 metres |
| 10Base2 | Thin coaxial cable | 180 metres |
| 10Base5 | Thick coaxial cable | 500 metres |
| 10BaseF | Fibre optic cable | 2000 metres |
| 100BaseT | Unshielded twisted pair | 100 metres |
| 100BaseTX | Unshielded twisted pair | 220 metres |
Then, we learned about Network Operating System.
Network operating system is
• Software that controls a network and its message (e.g. packet) traffic and queues, controls access
by multiple users to network resources such as files, and provides for certain administrative functions, including security.
There are two major types of network operating system. They are peer-to-peer system and client/server system. Click here to know more about them.
I think that's all for now..till then,,goodbye..>.<